What are the Main Causes of Boiler Accidents?
Major causes of boiler accidents can be due to failure of pressure parts of steam and water sides, safety valves failure, corrosion and degradation of boiler wall material, loose welded and non-tested joints.
The probability of which is very low (ONLY 0.5% OF THE ACTUAL ACCIDENTS) when you get your boiler for an Authorized Manufacturer complying to all the latest code construction of boilers such as ASME SEC I Div.1.
Poor water treatment causing scaling and overheating of the plates,
Low water levels, un-trained boiler operator, improper cleaning of the boiler furnace (WHEN IT COMES TO BIOSMASS FIRED BOILERS).
According to inspection records of various sources in the U.S., UK, and Europe in the late 19th and early 20th centuries the weakening of boilers due to simple scaling both water side and fired side was the most frequent cause of boiler accidents.
Also nowadays many unauthorized and illegal boiler alteration shops are manufacturing boilers which are very harmful, not only for the company also for the lives of the people as they are prone to catastrophic explosions. Hence, while buying boilers one should consider the certified boiler manufacturers over the local manufactures.
For clear understanding of failure associated with the boilers, an Ishikawa diagram for the root cause failure analysis of a steam boiler failure is shown below:
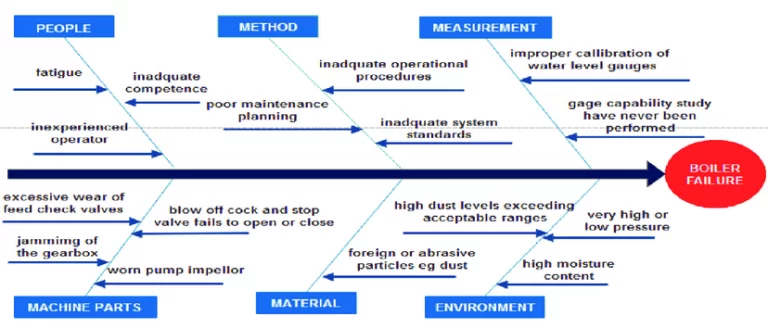
Some of other related failure causes are as follows:
Pressure Vessel Failure (OPERATIONAL ERROR / UNTRAINED STAFF)
The most common reasons for pressure vessel failure are excessive scale formation both water and fire side, low water levels, or corrosion or overheating of the metal. Damaged safety valves or water hammer may also have an effect on the vessel. When the vessel’s pressure range is compromised, it happens. To better grasp it, consider that a steam boiler working at 100 psig may expand water by a factor of 1500 from its initial volume. As a result, it generates a powerful force that results in dangerous boiler accidents.
Boiler Corrosion
Untreated water contains a sizable amount of dissolved oxygen, which is a major contributor to corrosion. The oxidation, scaling, and corrosion processes are accelerated by the high heat intensity of evaporation. Pitting corrosion causes boiler tube failures and may harm the equipment farther downstream.

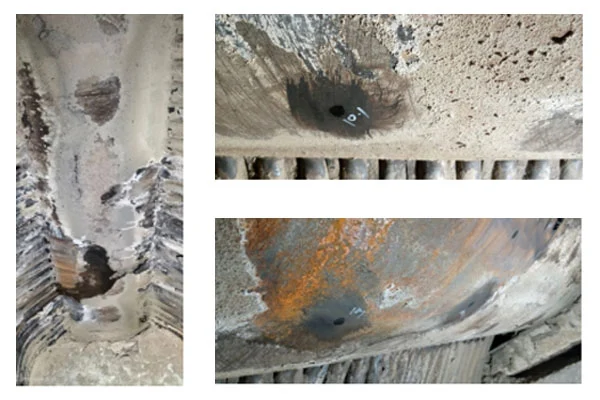
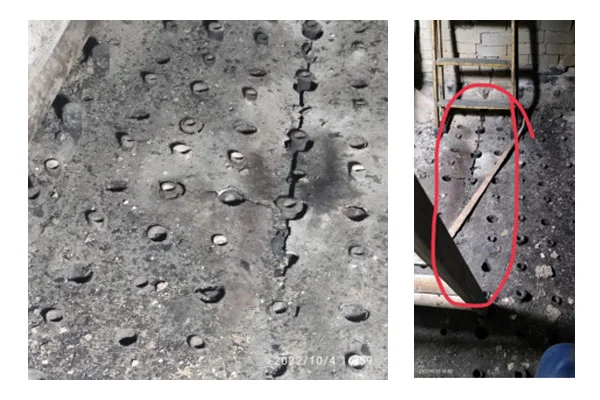
Accidents Due to Scaling on Furnace of Water Tube Boiler Running on Solid Fuel / Biomass
It is observed that when a boiler is operated on any solid fuel or biomass and the quality of the fuel is not controlled; unwanted deposits start to occur on the surface, walls of the furnace which results in poor heat transfer. If the boiler furnace is not properly cleaned than this results in overheating of the boiler resulting in hardness in material and cracking of water wall tubes of the furnace. This is the most common accident that is faced by companies who have untrained boiler operational staff.

Accidents Due to Choking of Furnace of Boiler Running on Solid Fuel / Biomass
It is observed that when a boiler is operated on any solid fuel or biomass and the quality of the fuel is not controlled i.e. sand, plastic or any item that has a higher melting point or cannot be burned other than the fuel being used for e.g. the roots of the tree the air nozzles on the bed of the furnace get chocked. If not properly cleaned that this will result in the overheating of the furnace bed of the boiler and ultimately result in a severe accident of the boiler. This is also a common accident that is faced by companies who have untrained boiler operational staff
Prevention of Boilers From Explosion
Following are some of the key parameters that can prevent Boilers from explosions:
- Regular Checking of Safety valves
- Proper insulation of heated parts of the Boiler
- Pressure Gauge monitoring
- Boiler ash tray and tubes cleaning on periodical basis to prevent them from scale formation
- Periodic maintenance of Boilers
- Proper treatment of Water before entering into the Boiler
- Boiler should not be operated at or above the maximum allowable pressure limits
- Boiler vents checking
- Check for LEL level and fuel line leakages before the ignition
- Trained and educated operational staff (most important)

