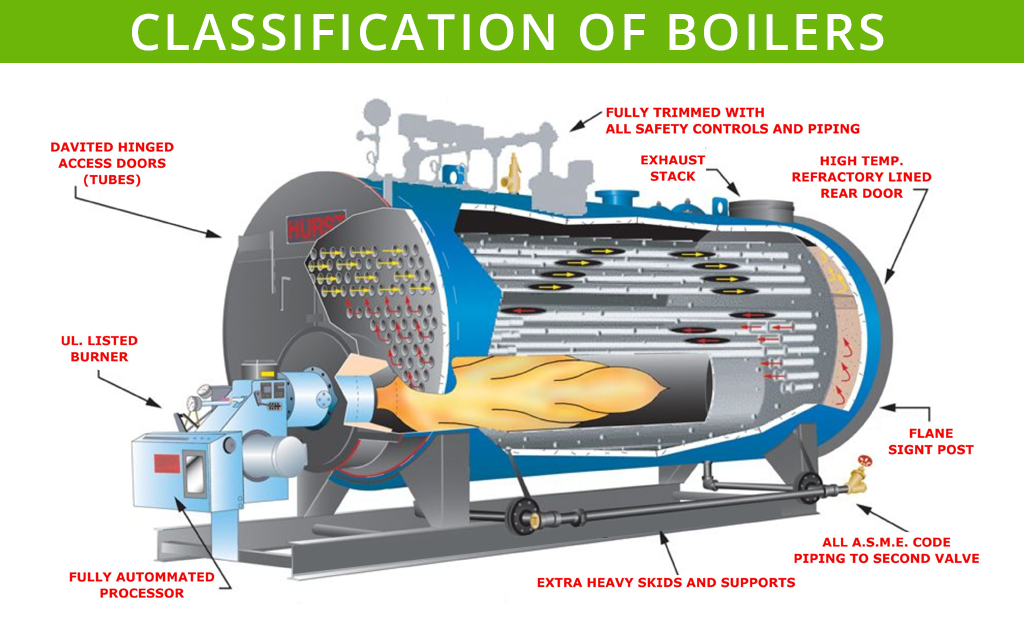
Boilers are essential pieces of equipment used in various industries for generating steam or hot water for various purposes. There are different types of boilers classified based on their design, fuel source, and operating principle. Forced circulation and induced circulation boilers are two such types of boilers that differ in their circulation mechanism.
In this blog, we will discuss the differences between a forced circulation boiler and an induced circulation boiler.
Forced Circulation Boiler:
In a forced circulation boiler,
- The circulation of water is achieved by using a pump to force the water through the boiler’s heat transfer surfaces.
- The pump ensures that there is a constant flow of water through the boiler, which helps to
maintain a uniform temperature throughout the boiler for efficient boiler operation.
- Forced circulation boilers are typically used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications where a large amount of heat needs to be transferred.
- One of the primary advantages of forced circulation boilers is that they can generate steam quickly and efficiently. This is because the constant flow of water through the boiler helps to transfer heat rapidly, and the pump ensures that there is no stagnant water in the boiler.
It is also necessary to have a deep knowledge of correct water temperatures so that the boiler could function properly. Maintaining the correct water temperature inside boiler is essential to prevent corrosion.
- Forced circulation boilers are also relatively compact and require less space compared to other types of boilers.
- The high flow rates of water required in these boilers make them more susceptible to erosion, corrosion, and scaling. This can lead to reduced efficiency, increased maintenance costs, and potentially, premature failure of the boiler.
- The use of a pump in forced circulation boilers can increase the power consumption and operating costs of the system.
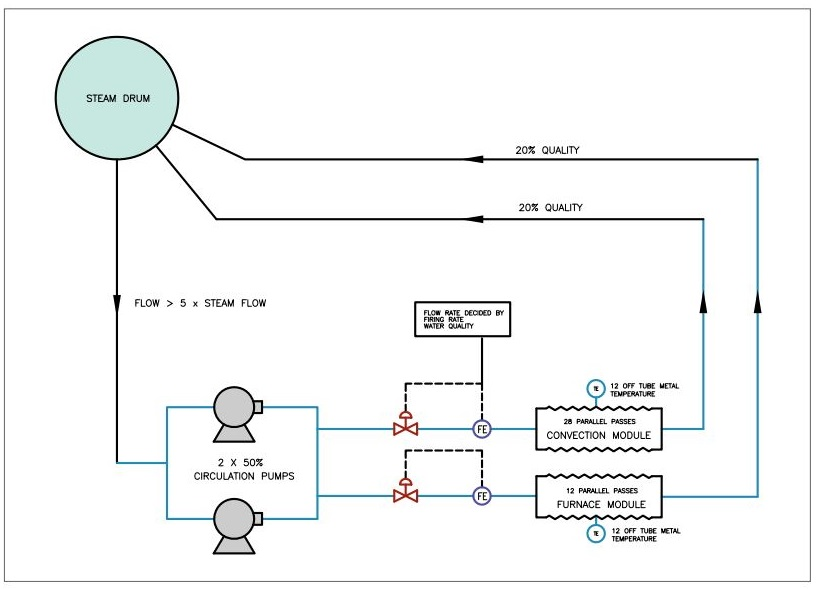
Induced Circulation Boiler:
- In an induced circulation boiler, the circulation of water is achieved by using a steam-driven or electrically driven pump to induce a flow of water through the boiler.
- The pump draws water from the boiler’s drum and forces it through the boiler’s heat transfer surfaces before returning it to the drum.
- The steam-driven pump is powered by the steam generated by the boiler, while the electrically driven pump is powered by an external power source.
- One of the primary advantages of induced circulation boilers is that they are more resistant to scaling, erosion, and corrosion compared to forced circulation boilers. This is because the flow rate of water in these boilers is relatively low, which helps to reduce the risk of these issues.
- Induced circulation boilers can operate at lower pressures and temperatures compared to forced circulation boilers, which can help to reduce the cost of the system.
- The use of a pump to induce the flow of water through the boiler can increase the risk of pump failure, which can lead to a loss of circulation and potentially, overheating of the boiler.
- The lower flow rates of water in these boilers mean that they may take longer to generate steam compared to forced circulation boilers.
Conclusion:
In summary, forced circulation and induced circulation boilers differ in their circulation mechanism. Forced circulation boilers use a pump to force water through the boiler’s heat transfer surfaces, while induced circulation boilers use a pump to induce a flow of water through the boiler.
Each type of boiler has its advantages and disadvantages, overall, the choice between forced circulation boiler and induced circulation boiler depends on various factors such as the required flow rate, pressure, temperature, the risk of scaling, erosion, and corrosion, and the specific application’s requirements. Consultation with a professional engineer or boiler expert like Solarkaz International is recommended before choosing the right boiler for a particular application