The heat exchanger is used for transferring heat from one medium to another medium. A heat exchanger acts as a cooler or warmer for a fluid and it can be used in many different applications such as power plants, refrigeration systems, air conditioning, and heating systems, mining systems, and food industries. Today many of the industries are even using waste heat recovery systems in boilers which also serve the purposes of heat exchanging between two systems for example, the outlet of the boiler is connected with the economizer to enhance the overall efficiency of the boiler. Hence, heat exchangers are very beneficial for any industry.
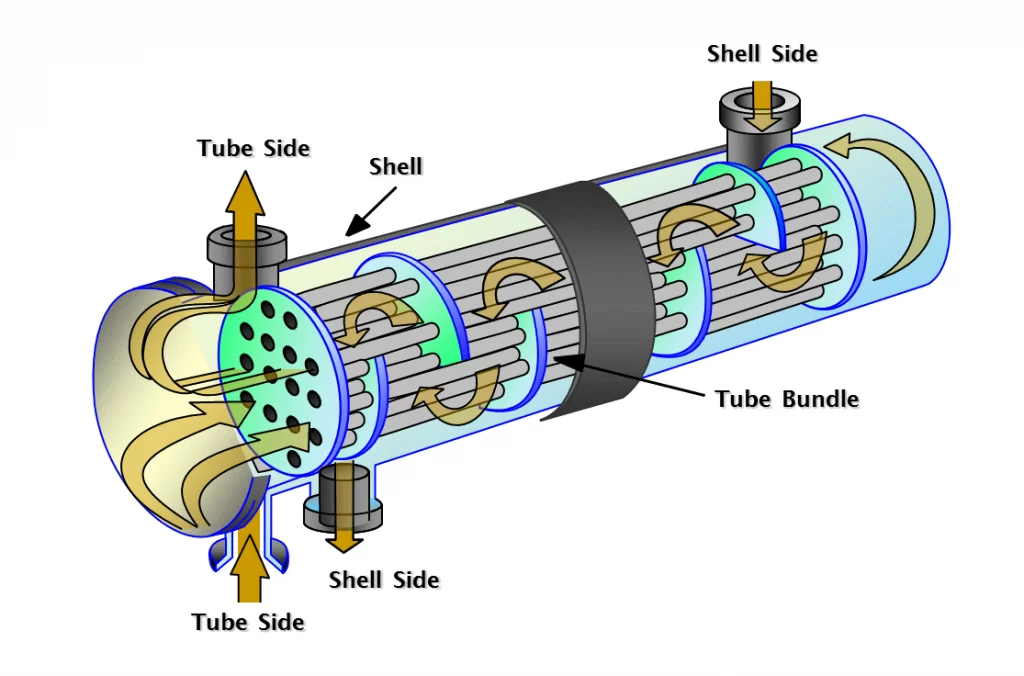
The Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger is a solid-wall heat exchanger with a proper shell and tube-type structure. It operates with a top and bottom loop of tubing and has two fluid passages through the core. This design allows heat transfer without an intermediate step in between the heat source and multiple destinations, making it more efficient than other types of heat exchangers.
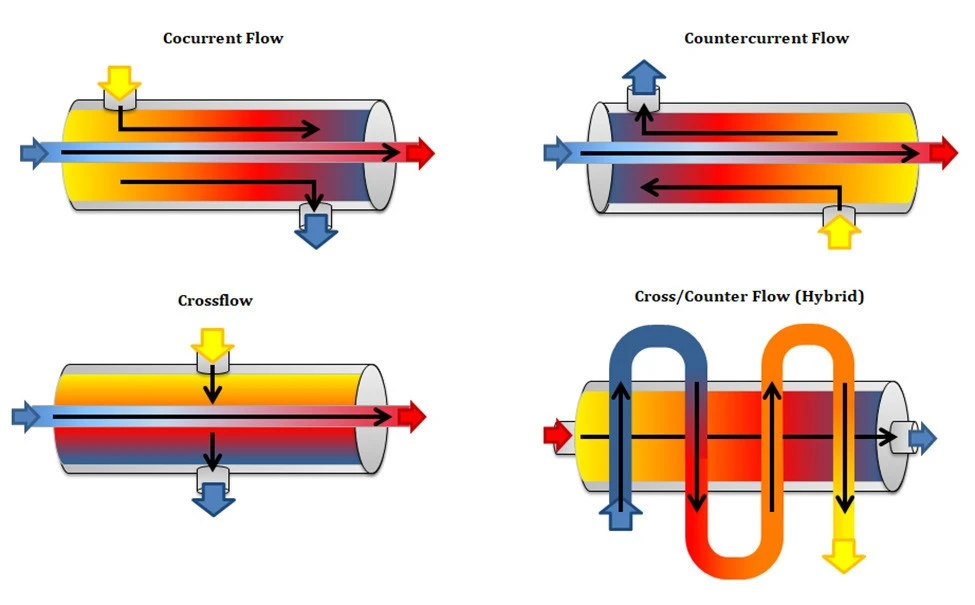
Classification of Heat Exchangers by Flow Configuration
Cocurrent Flow
In cocurrent flow type heat exchanger, the streams flow parallel to each other and in the same direction. This is less efficient than countercurrent flow but does provide more uniform wall temperatures.Cross Flow
Crossflow heat exchangers are intermediaries in efficiency between countercurrent flow and parallel flow exchangers. In these units, the streams flow at right angles to each other
Countercurrent Flow
Countercurrent flow exchanger is one in which the two fluids flow parallel to each other but in opposite directions. This type of flow of arrangement allows the largest change in temperature of both fluids and is therefore most efficient.Cross/Countner Flow
In counter flow type of heat exchanger, the two fluids flow parallel to each other, but in opposite directions.
Why Baffles Are Used In Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers?
✔️ To support the tube
✔️ To direct the fluid stream across the tube
✔️ To improve the rate of heat transfer
Advantages of Heat Exchanger
✔️ High Efficiency
✔️ High operating pressures
✔️ More heat transfer between the different sources
✔️ Less Costly than others
Limitations of Heat Exchanger
✔️ Large size
✔️ More space is needed for cleaning
✔️ Difficult to clean Shell Side
Heat Exchanger Problems
1. Heat Exchanger Fouling
Fouling is the formation of unwanted material deposits on heat transfer surfaces of tubes during process heating and cooling. Fouling might contain materials that consist of either living organisms or non-living organisms.


Types of Fouling
✔️ Incrustation
✔️ Scaling
✔️ Sediment
✔️ Biological Growth
Reasons of Fouling
✔️ Variable water pH✔️ Product viscosity
✔️ The Roughness of component surfaces
Solutions
✔️ Using cleaning agents for removing the scaling and incrustation✔️ Removing sediments
✔️ Using a chemical cleaning process or water treatment method to remove biological growth
2. Corrosion


Solution
Selecting the material with adequate corrosion resistance for the environment along with using proper treatment chemicals.
3. Vibration
Heat exchangers should not be placed near equipment such as air compressors or mechanical chillers because excessive vibrations from these machines can cause tube failures.
Conclusion
Shell and tube type heat exchangers are used widely in the industrial market and are the most commonly available heat exchangers within the markets due to the high demands. Also, the maintenance of these heat exchangers is very easy compared to the other heat exchangers.
Solarkaz International is providing the best solution for Heat Exchangers throughout the markets, which is valuable in regard to the total cost of ownership. We had several clients all over the world, and we are competent in building Heat Exchanger designs as per International Standards.
Looking for the Heat Exchangers? Contact us to know more about the Heat Exchangers.

